Youth handball development is not a miniature version of adult handball. Young players learn differently, have different physical capabilities, and need different motivational approaches. Following structured development pathways creates better players while keeping them engaged with the sport long-term.
Age-Based Development Stages
IHF-recommended progression:
Mini Handball (6-8): Focus on fun, basic motor skills, and introduction to ball handling.
Junior (8-10): Fundamental throwing, catching, and simple tactical concepts.
Youth (10-12): Position introduction, basic systems, and cooperative play.
Intermediate (13-15): Technical refinement, tactical understanding, and competition readiness.
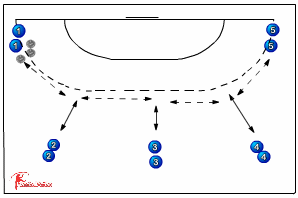
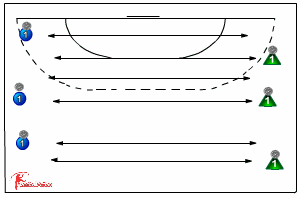
Fundamental Movement Skills
Building athletic foundations:
Coordination: Balance, agility, and spatial awareness.
Ball skills: Catching, throwing, and dribbling with both hands.
Running patterns: Change of direction, acceleration, and deceleration.
Body control: Landing mechanics and contact preparation.
Creating Positive Experiences
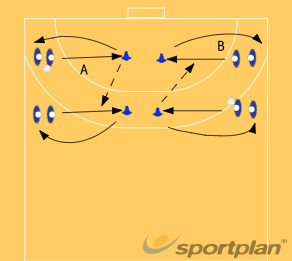
Game-based learning: Small-sided games provide maximum touches and engagement.
Success design: Activities where players succeed frequently.
Social element: Team activities build friendships and commitment.
Varied activities: Prevent boredom through creative session design.
Coach Development for Youth
Specialised training: Youth coaches need specific education in child development.
Communication skills: Age-appropriate instruction methods.
Safety awareness: Appropriate training loads and injury prevention.
Positive environment: Create culture that retains young players.
Key Coaching Points
- Match activities to developmental stage, not just chronological age
- Fun and engagement are essential for retention
- Fundamentals first - specialisation comes later
- Small-sided games maximise learning opportunities
- Youth coaches require specialised training and support